cmd commands: Display IP and network connections

With simple commands a quick overview of the current network settings can be read out, and thus possible connection errors can be found, or an overview of other devices in the network can be obtained. The commands described here are cmd commands for Windows. They are entered via the command prompt: cmd.
Aim of this article Effort Prerequisite
in the command prompt
and a Windows computer

How to display a list of all network connections?
The command: netstat -ano prints a list of all network connections.
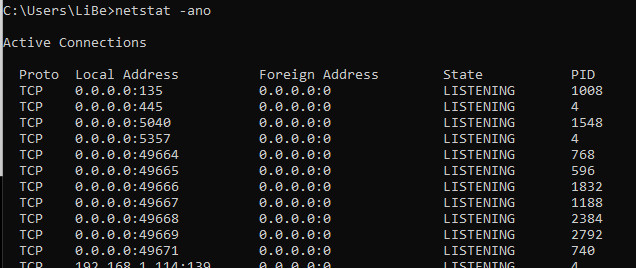
Legend:
| Lokale Adresse | Connection from the address |
|---|---|
| Foreign Address | Connection to the address with the indicated port (The port is after the ":" ) |
| State | For example, listening means that the computer is listening at this address, i.e. it is waiting for a connection; established means that there is an active connection here. |
| PID | To identify the programs behind it, the PID (Process Identification) is on the right. |
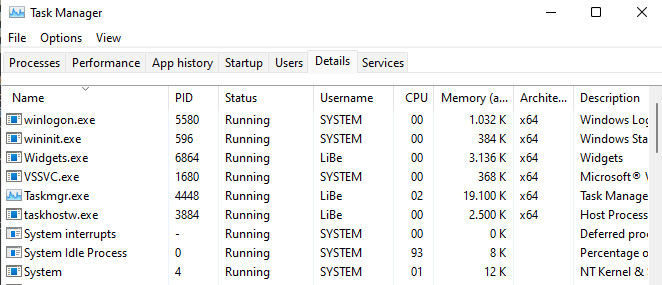
The program for the PID can be displayed either in the Task Manager or by means of the parameter /b.
To do this, open the Task Manager with [Ctrl-Alt-Del]. In Windows 10 you can find the PID under Details and possibly under Services.
The PID may have to be displayed using Select columns.
see also: show active network connections and processes | Windows
How can the IP address be determined?
The IP address or network address can be read out with the ipconfig command:
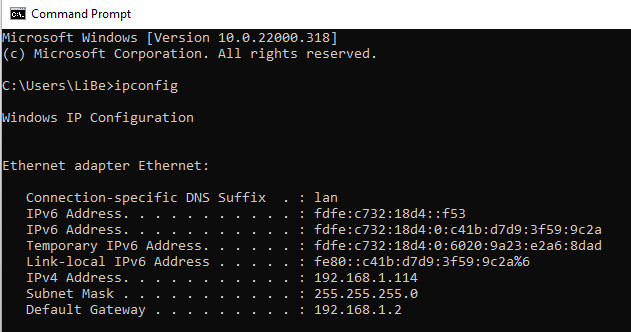
Relevant is usually the IPv4 address, which has the following format ???.???.???.???, where ??? are each 3 numbers from 0-255. (In the screenshot 192.168.1.114)
IPv4 should be replaced by IPv6 in the long run, but it stubbornly persists and is typically in use. In the rarest cases, IPv6 is used for a home network.
The standard gateway is also interesting at this point. The standard gateway connects other networks, it forwards requests that cannot be answered by the local network. Mostly the standard gateway leads to the internet.
The router can be managed by calling the address in a browser.
How can the MAC address be determined?
The MAC address is a unique address of the network adapter. The MAC address can be displayed using the getmac command or with ipconfig /all.
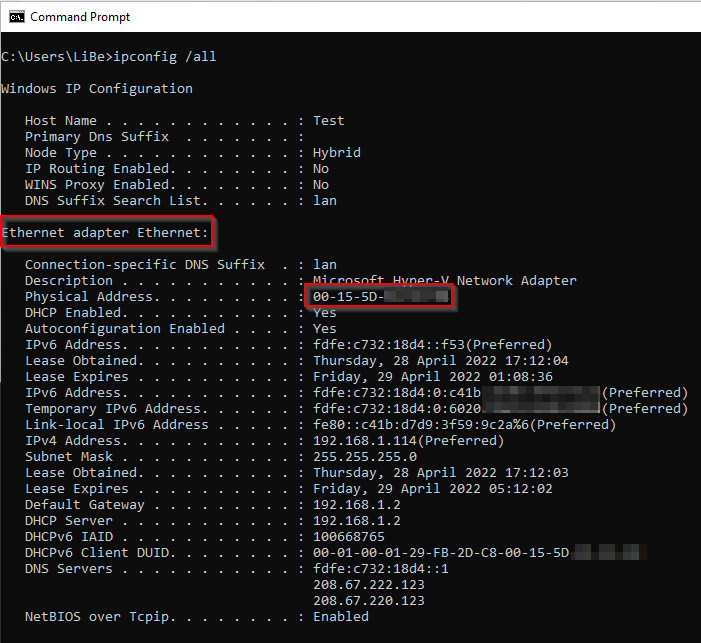
Usually a laptop has several network cards, e.g. the WLAN adapter (wireless LAN adapter) and an RJ45 network card: Ethernet adapter.
The respective MAC address can be found under "Physical address".
How to test the network connection?
To test the connection to another network device, a ping can be sent: Ping requests a response from the network device and measures the time until it comes back (RTT: Round trip; latency). ping ???.???.???.???
???.???.???.??? is the IP address
E.g. ping 192.168.0.1
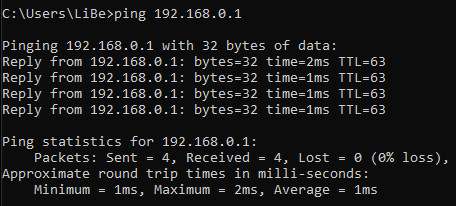
Pinging 192.168.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received =4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), ...The answer in this case is: the device with 192.168.0.1 is reachable and is in the immediate vicinity, because time<1ms
How can the MAC address be determined from the IP address?
To display the MAC address, the network device must be contacted first, for example by pinging the IP address(ping ???.???.???.???). When contacting a client, the ARP cache is filled, which represents a list of IP addresses and the associated MAC addresses.
The arp -a command outputs a list of IP addresses and the associated MAC addresses.
Interface: ???.???.???.??? --- ??????
| Internetadresse | Physikal. Adresse | Typ |
|---|---|---|
| ???.???.???.??? | xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx | dynamic |
| ???.???.???.??? | xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx | dynamic |
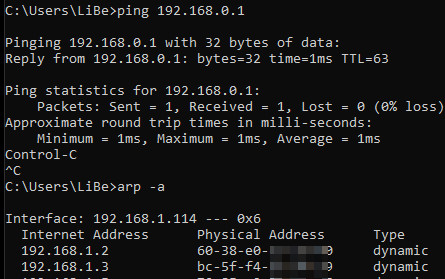
also here with "physical address" the MAC address is meant.
How to display the routing table?
The route print command lists all active routes of the routing table.
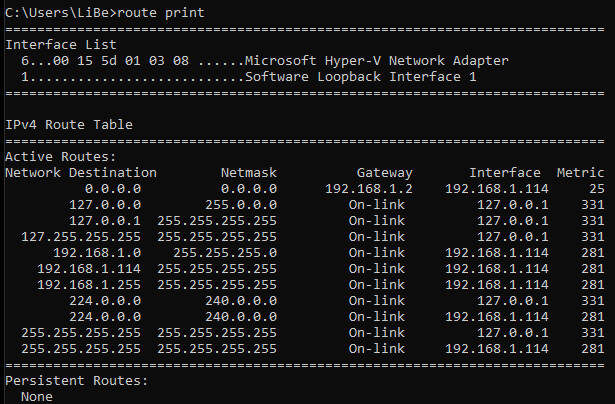
Routing is used to assign networks to the various network adapters.
By interface is meant, for example, a network adapter and its associated IP address.
The route add command can be used to assign specific networks to specific interfaces.
The default gateway, for example, is used if no entry exists for a certain network, i.e. all networks. The default gateway always appears with the network destination 0.0.0.0 and with a network mask of 0.0.0.0.
How to find out the IP address of a hostname or domain?
The nslookup command can be used to query a DNS server for a domain for its IP address.
How to start a route tracing ?
The tracert command traces routes to the domain (which servers, routers, ... are traversed to the domain). E.g. tracert www.libe.net traces all routes to this web server.
How to display all connected network drives ?
By means of the netuse command, connected network drives can be displayed
How to display open sessions on the server?
The command: net session (in the command prompt) can be used to display open network sessions, for example drive connections, on the server.
further topics
 ({{pro_count}})
({{pro_count}})
{{percentage}} % positive
 ({{con_count}})
({{con_count}})