Webhook: curl and cron
a simple cron job (Scheduled Tasks) on an Openwrt access point, everything that the Linux terminal makes available can be transmitted to Home-Assistant. As an example, my OpenWrt devices provide the following information:
- The list of all connected clients.
- CPU and memory utilization.
- The last entry in the kernel log.
- The DHCP leases from the main router.
- Usteer data from the main router for the network overview.
The cron job starts every minute and enables continuous monitoring of the network infrastructure via Home Assistant.
Basics for this implementation, see: Display datafrom any Linux systems in HA
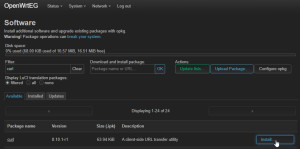
Prerequisite on the access points: curl
To enable the access points to send data to a webhook in Home Assistant, only the small software package "curl" is required:
Once curl has been installed, any commands can be transmitted to Home Assistant every minute, for example via Scheduled Tasks:
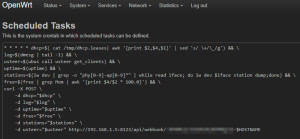
Scheduled Tasks
I use the following commands in the Scheduled Tasks on the access points to collect the data. The commands can be adapted as required or extended with additional commands. It makes sense to test the commands in a terminal beforehand.
* * * * * log=$(dmesg | tail -1) && \
uptime=$(uptime) && \
stations=$(iw phy1-ap1 station dump && iw phy1-ap0 station dump && iw phy0-ap0 station dump) && \
free=$(free | grep Mem | awk '{print $4/$2 * 100.0}') && \
curl -X POST \
-d log="$log" \
-d uptime="$uptime" \
-d stations="$stations" \
-d free="$free" \
http://192.168.1.5:8123/api/webhook/MySuperSecret-$HOSTNAME
I have added additional commands to the OpenWrt device with active DHCP so that the device transmits the DHCP leases and also the Usteer data of all connected clients:
* * * * * dhcp=$( cat /tmp/dhcp.leases| awk '{print $2,$4,$1}' | sed 's/ \+/\_/g') && \
log=$(dmesg | tail -1) && \
usteer=$(ubus call usteer get_clients) && \
uptime=$(uptime) && \
stations=$(iw dev | grep -o "phy[0-9]-ap[0-9]*" | while read iface; do iw dev $iface station dump;done) && \
free=$(free | grep Mem | awk '{print $4/$2 * 100.0}') && \
curl -X POST \
-d dhcp="$dhcp" \
-d log="$log" \
-d uptime="$uptime" \
-d free="$free" \
-d stations="$stations" \
-d usteer="$usteer" http://192.168.1.5:8123/api/webhook/MySuperSecret-$HOSTNAMETo ensure that the command block can be used on all access points without adaptation, I also use the host name for the webhook secret. This allows me to use the same secret for all access points and still use a separate webhook for each device in Home Assistant. The client secret "???" and the IP address of Home Assistant must of course be adapted accordingly, whereby the client secret can be freely selected. The combination of secret and host name activates the respective trigger and makes the transmitted data available in its automation.
Receiving the data in Home Assistant:
So that data larger than 255 characters can also be processed, which is the case for the DHCP leases and Usteer data, I use the HACS integration "Variables+History", see: Display datafrom any Linux system in HA
I have created the following sensors for reception:
For the main router:
- input_text.openwrt_log (last log line of the kernel log, standard helper sensor)
- sensor.openwrt_load (CPU utilization, Variables+History Sensor)
- sensor.openwrt_ram (RAM utilization, Variables+History Sensor)
- sensor.openwrt_crondata (DHCP and Usteer data, Variables+History Sensor)
and for the access points:
- input_text.APNAME_log (Standard Helper Sensor)
- sensor.APNAME_load (Variables+History Sensor)
- sensor.APNAME_ram (Variables+History Sensor)
The automation for filling the sensors looks as follows:
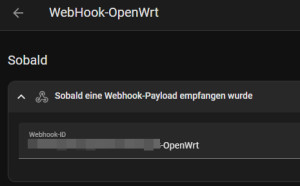
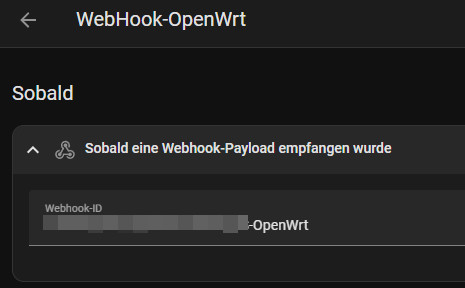
alias: WebHook-OpenWrt
description: ""
triggers:
- trigger: webhook
allowed_methods:
- POST
- PUT
local_only: true
webhook_id: "???-OpenWrt"
conditions: []
actions:
- action: input_text.set_value
metadata: {}
data:
value: "{{ trigger.data.log }}"
target:
entity_id:
- input_text.openwrt_log
- action: variable.update_sensor
metadata: {}
data:
replace_attributes: true
attributes:
dhcp: "{{ trigger.data.dhcp }}"
usteer: "{{ trigger.data.usteer }}"
stations: "{{ trigger.data.stations }}"
value: >-
{% set Stations = trigger.data.stations.split('Station ') %} {% for
Station in Stations if (Station.split("\n")[0].split(" (")[0] != "")%}
{% set StationDetail = Station.split("\n") %}{% set mac =
StationDetail[0].split(" (")[0] %}{{ mac.replace(":","") }}{% endfor %}
target:
entity_id: sensor.openwrt_crondata
- action: variable.update_sensor
metadata: {}
data:
replace_attributes: false
value: "{{ trigger.data.uptime.split(\": \")[1].split(\",\")[0] }}"
target:
entity_id: sensor.openwrt_load
- action: variable.update_sensor
metadata: {}
data:
replace_attributes: false
value: "{{100 - trigger.data.free | float}}"
target:
entity_id: sensor.openwrt_ram
mode: parallel
max: 10
The automation of the access points is the same, with the exception of the DHCP and Usteer data.
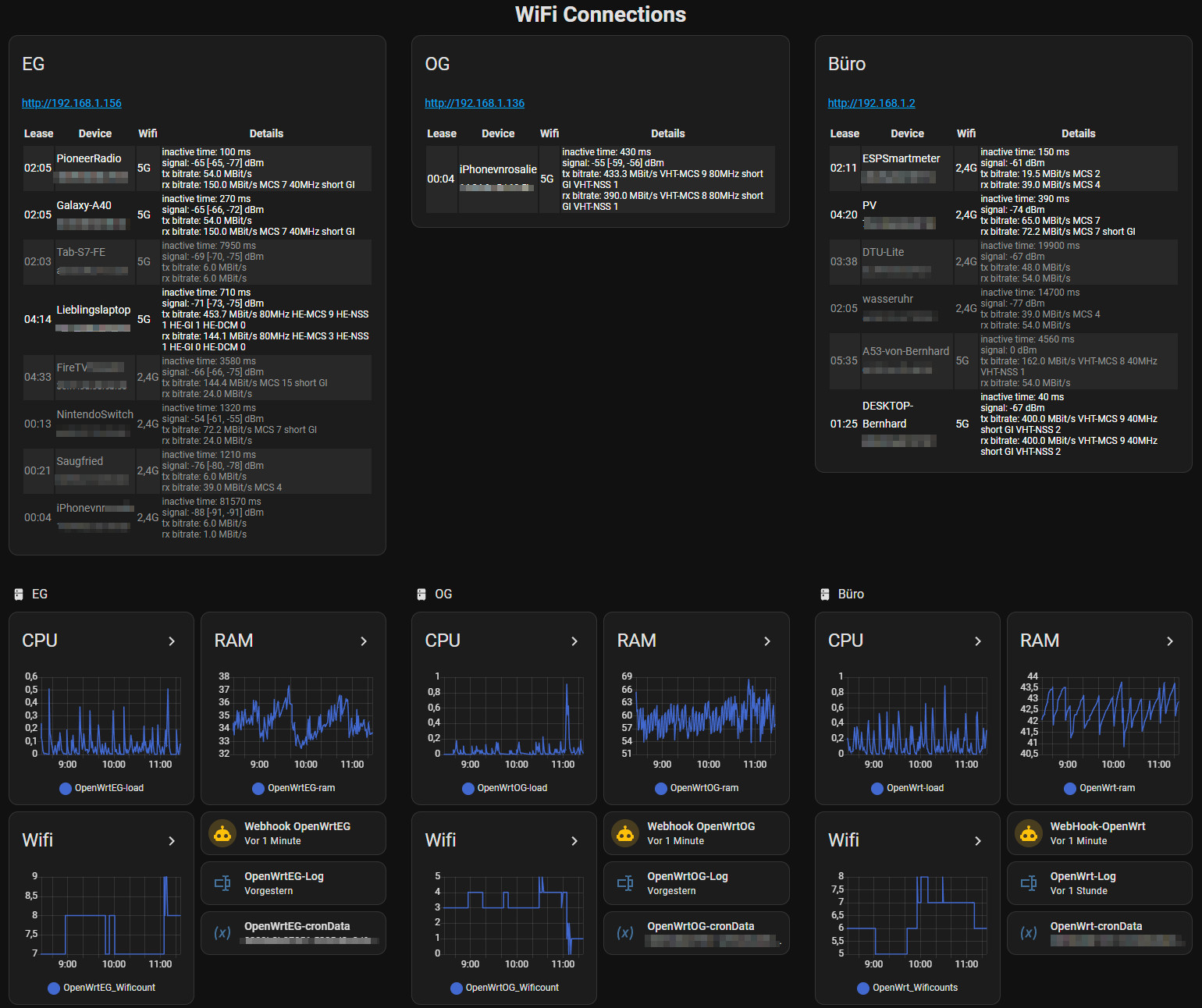
Dashboard
I then created the following markdown card for each of the access points:
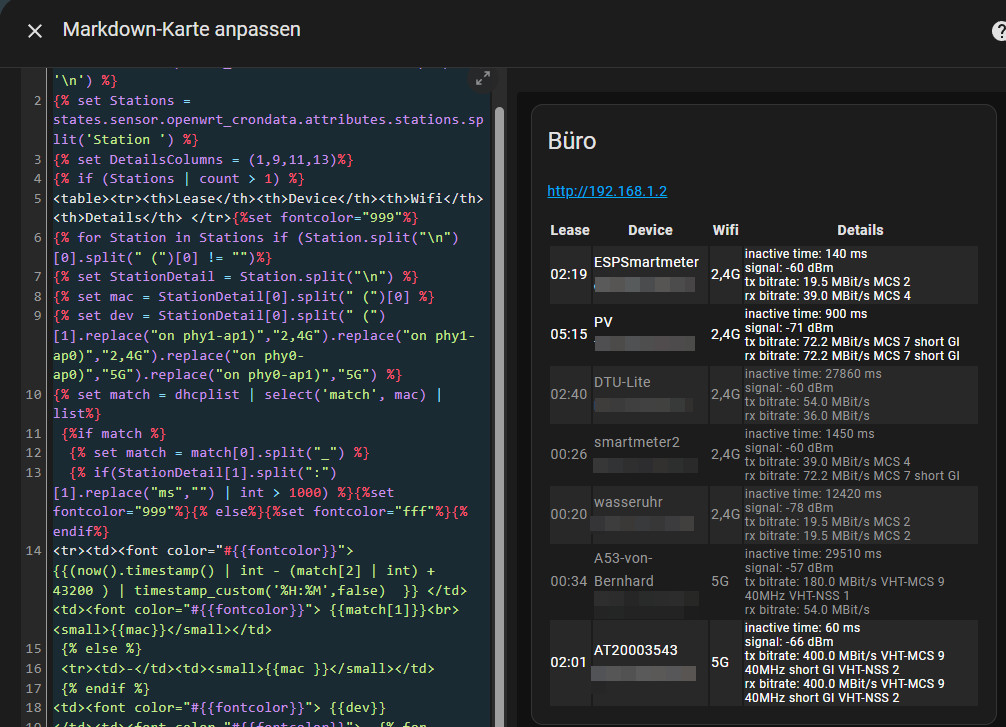
{% set dhcplist = states.sensor.openwrt_crondata.attributes.dhcp.split('\n') %}
{% set Stations = states.sensor.openwrt_crondata.attributes.stations.split('Station ') %}
{% set DetailsColumns = (1,9,11,13)%}
{% if (Stations | count > 1) %}
{%set fontcolor="999"%}
{% for Station in Stations if (Station.split("\n")[0].split(" (")[0] != "")%}
{% set StationDetail = Station.split("\n") %}
{% set mac = StationDetail[0].split(" (")[0] %}
{% set dev = StationDetail[0].split(" (")[1].replace("on phy1-ap1)","2,4G").replace("on phy1-ap0)","2,4G").replace("on phy0-ap0)","5G").replace("on phy0-ap1)","5G") %}
{% set match = dhcplist | select('match', mac) | list%}
{%if match %}
{% set match = match[0].split("_") %}
{% if(StationDetail[1].split(":")[1].replace("ms","") | int > 1000) %}{%set fontcolor="999"%}{% else%}{%set fontcolor="fff"%}{% endif%}
{% else %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
| Lease | Device | Wifi | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| {{(now().timestamp() | int - (match[2] | int) + 43200 ) | timestamp_custom('%H:%M',false) }} | {{match[1]}} {{mac}} |
||
| - | {{mac }} | {{dev}} | {% for DetailsColumn in DetailsColumns %} {{StationDetail[DetailsColumn].split(":")[0]}}:{{StationDetail[DetailsColumn].split(":")[1]}} {% endfor %} |
{% else %}
keine Verbindungen ..
{% endif %}The sensor name, in this case "sensor.openwrt_crondata", must of course be created in advance for each access point and adjusted here.
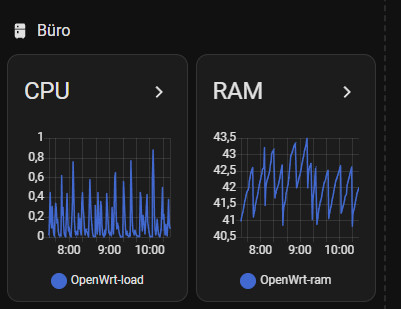
The counters for CPU and RAM can also be used for the charts:
Conclusion
The use of webhooks in conjunction with curl and cron enables effective monitoring of Linux-based network systems in Home Assistant. By regularly transferring network data such as CPU and RAM utilization, connected clients and DHCP leases, the network infrastructure always remains up-to-date. The implementation is simple and only requires the installation of curl on the access points.
 ({{pro_count}})
({{pro_count}})
{{percentage}} % positive
 ({{con_count}})
({{con_count}})